Waveshapers are a great way to enrich the harmonics of any electric instrument and create a unique sound signature. You’ve probably used effects employing waveshaping countless times when making music without even knowing it!
When you start delving into the world of waveshapers, it’s easy to get lost in the sea of mathematical functions and equations. In this article, we'll explore the concept of waveshaping in simple terms and show you how you can use it to create a unique sound.
Waveshaper: The Name Says It All
The first thing to remember is that a waveshaper does precisely what its name implies: it manipulates soundwaves, bringing to life more articulated sounds.
In digital audio production, wave-shaping is done by changing a digital signal in a way that enhances its harmonic content. It’s a sound synthesis technique that changes an original waveform to create additional harmonics.
Distortion and saturation fall under the umbrella of waveshaping, as these effects are, in fact, manipulating the soundwave. What a waveshaper offers more than a saturation plugin is more control over how the signal behaves, allowing you to control the harmonic content fully.
Depending on the shaping curve, the waveshaper can add both odd harmonics and even harmonics to the sound by applying specific transfer functions. For instance, using polynomial waveshaping functions can help generate only even harmonics or odd harmonics, depending on the polynomial used. More on that later.
The Nature of Digital Audio
Understanding how sounds are recorded digitally is crucial if you want to know how waveshapers work.
We call a sound “digital audio” when it’s stored and processed on computers and other electronic devices. Unlike analog sound, which is a smooth and continuous signal, digital audio breaks sound down into tiny snapshots called samples. Basically, these samples are individual pictures of the sound taken at specific times.
Two things define the quality of digital audio: sample rate and bit depth.
Sample rate is the number of samples taken each second to create the digital version of the sound. It's measured in Hertz (Hz), and a higher sample rate means better sound quality.
For example, music CDs use a sample rate of 44,100 samples per second. The higher the sample rate, the better wave-shaping tools can process high-frequency components, reducing aliasing and producing a cleaner output signal.
Bit depth controls how detailed each sample is. The more bits, the more detailed and accurate the sound can be. This is crucial for capturing both quiet and loud parts of a sound.
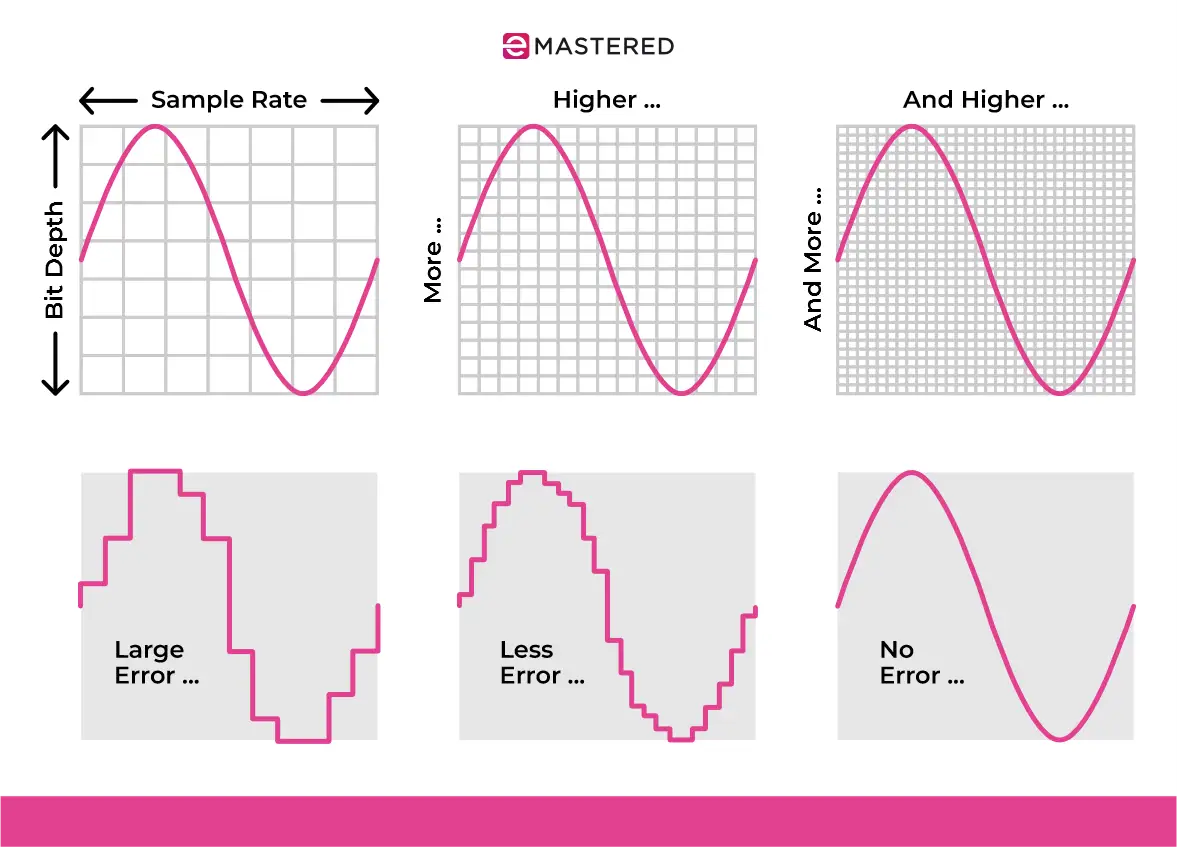
A higher bit depth gives more control over the amplitude, which is especially important when applying waveshaping functions to create smooth or complex waveforms without introducing unwanted noise or artifacts.
So, how do waveshapers affect the waveform?
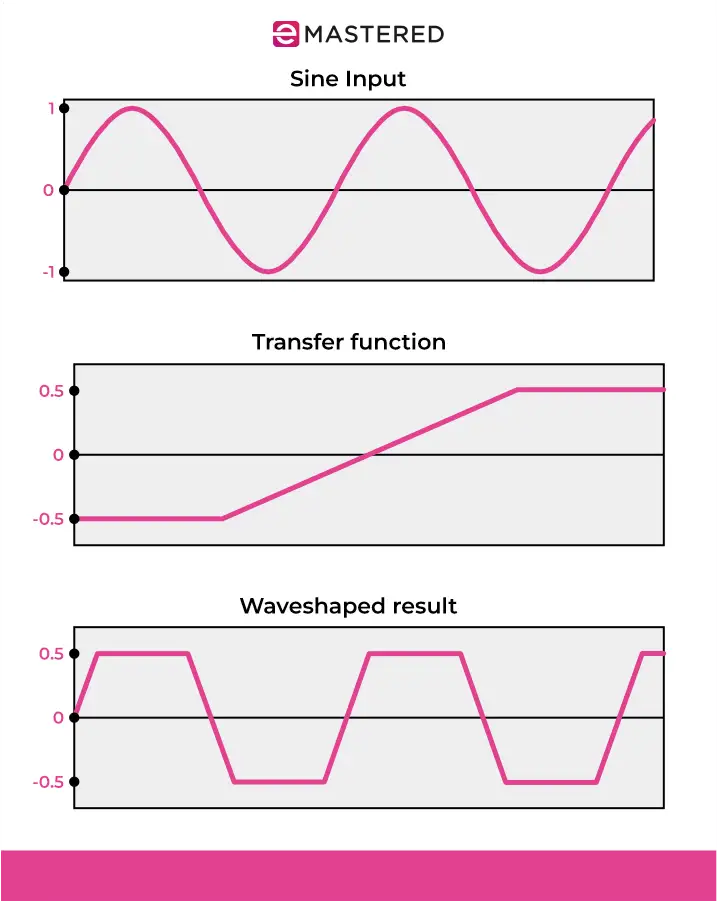
They change the waveform by applying a waveshaping function to the signal. This shaping function can be adjusted to enhance specific harmonics or create entirely new timbres.
Starting with a simple sine wave input and applying a wave shaping function can generate a richer spectrum of harmonics, transforming a simple tone into a more complex sound.
As you might have guessed, the level of control you have over the waveform is far superior with a waveshaper than with a regular distortion or saturation effect.
By carefully selecting and adjusting the wave shaping function, you can predict and manipulate the harmonic content, creating anything from analog-like warmth to aggressively distorted textures.
Various Waveshaping Techniques
The next section might be a bit overwhelming if you're not familiar with mathematical functions.
A transfer function is a mathematical formula that defines how a signal should be altered to produce an output signal. Depending on the wave shaping transfer function used, you'll get different outputs. Here are a few common techniques:
Polynomial Waveshaping
Polynomial wave shaping is called this way because it applies polynomial equations to transform the input signal.
The sound output is a function of the input signal raised to a power, which enhances a waveform with extra harmonics.
For the sake of simplicity, let’s use a sine wave as the input signal. By applying a cubic polynomial function (e.g., y=x3y = x^3y=x3), the sine wave is distorted, introducing third-order harmonics.
This can add a rich, analog-like distortion, enhanced by the odd harmonics in the output spectrum.
Exponential Waveshaping
Exponential wave shaping applies an exponential function to the signal, which gives you a sharp distortion. The intensity of the effect is controlled by the base of the exponential function.
Following the same example we used for polynomial wave shaping, if you apply an exponential function like y=ex−1y = e^x - 1y=ex−1 to a sine wave, the waveform is reshaped to create a more aggressive sound with high harmonic content (i.e. with sharp corners).
This type of shaping function is great if you want to create high-frequency harmonics with a more distorted output.
Lookup Table Waveshaping
Perhaps the most complex wave shaping function, lookup table wave shaping matches input signal values to a predefined set of output values stored in a table, which brings to life complex, non-linear transformations.
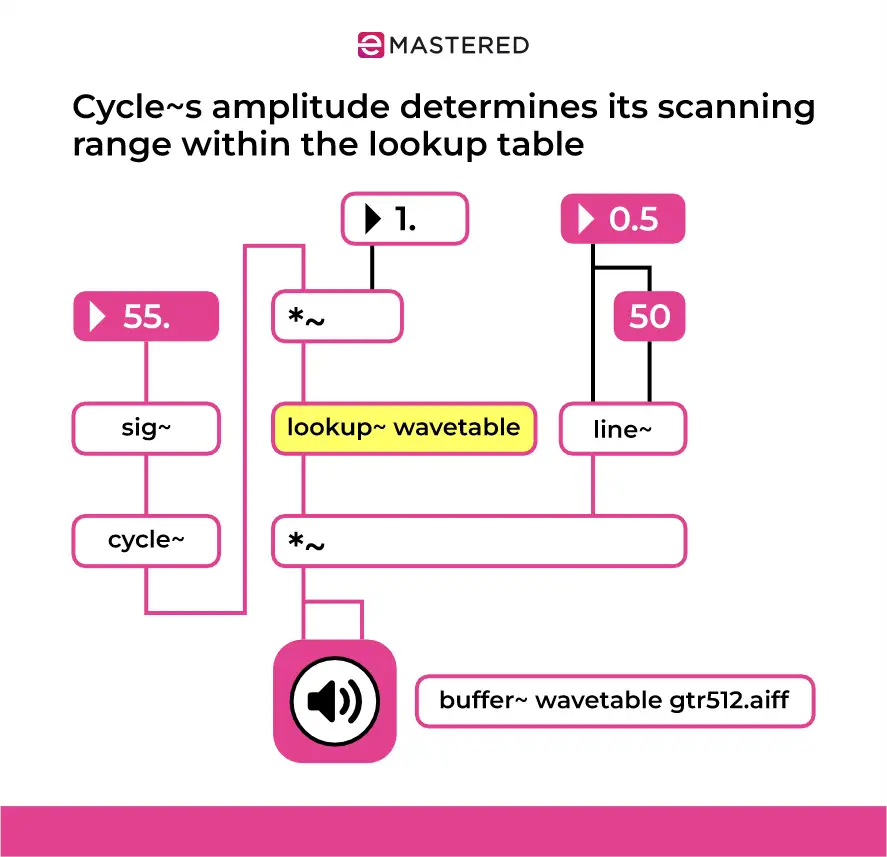
Here, the sine wave’s input values are mapped to a curve defined by the lookup table. This can produce unpredictable and highly customizable sounds, which is why experimental composers love it.
Lookup table wave shaping allows you to design unique waveforms that can't be easily achieved with simple polynomial or exponential functions, giving you the power to create entirely new spectra of sound.
How to Master Waveshaping
Let’s identify the steps necessary to master the art of wave shaping in chronological order:
Know all the Waveshaping Functions
Different wave-shaping functions produce different harmonic structures.
Understanding and predicting how a waveform will change based on the function you use will help you create the desired sound without spending hours shaping soundwaves.
Start simple. Use a sine wave as your base signal and start applying different wave-shaping functions. Keep track of how each function changes the waveform and the sound it brings to life.
It’s crucial to use a spectrum analyzer, especially if you’re a beginner. The visual feedback will help you understand how wave shaping affects the sound and make it easier to achieve the desired sound.
For example, when applying a function to a sinusoidal input, you can directly observe the new harmonic content that appears in the frequency spectrum, helping you understand how different shaping parameters affect the sound.
Try Different Input Signals
Sine waves, square waves, and complex waveforms will all react differently to the same wave-shaping function.
Since the effect of wave shaping changes according to the input signal, try to apply the same wave shaping function to a sine wave and a sawtooth wave, and pay attention to the differences in the harmonic content.
This practice will help you understand how different waveforms are transformed and how to predict the results of wave shaping on different sounds.
Built-In Waveshaping Tools
Most DAWs come with wave-shaping tools that are perfect for getting started.
Ableton Live is one of the most popular DAWs and comes with a Saturator that allows you to apply different wave-shaping curves and even draw your own.
If you want to give it a try, start from the default “Analog Clip” setting to a bassline, then tweak the curve or switch to a different mode (like “Soft Sine”) to see how the sound changes.
Best Waveshaping Software
FabFilter Saturn 2
FabFilter Saturn 2 is a fantastic distortion and wave-shaping plugin that offers plenty of distortion styles and multi-band audio processing. It also comes with endless modulation options for shaping the sound on your own.
The Saturn 2, an evolution of the already excellent FabFilter Saturn, features a redesigned interface, additional distortion styles, enhanced envelope generators, and better modulation capabilities.
The plugin provides precise control over the harmonic content and spectra of your audio, regardless of whether you're looking for subtle warmth or extreme distortion.
Serum (Xfer Records)
Serum is an excellent wavetable synthesizer with exceptional wave-shaping capabilities through its Warp modes.
You can apply various wave-shaping algorithms like Bend, Mirror, or Sync directly to the wavetable, changing the coefficients in real-time. To do that, load a basic wavetable in Serum and apply the "Bend +" Warp mode. As you increase the amount, the waveform will bend and change shape, introducing new harmonics.
Serum enhances creative manipulation of the input waveform, offering real-time visual feedback so you can see exactly how your changes affect the output signal.
Waves MetaFilter
Waves MetaFilter combines filtering with wave shaping, allowing you to shape the sound as it’s filtered.
You can add distortion to the filtered signal, which will give you aggressive textures that can evolve organically and in unpredictable ways. This affordable plugin offers plenty of shaping functionalities, envelope following, LFO and sequencer control, drive, bit-crushing options, delay, sidechain, and MIDI learn.
u-he Zebra 2
Zebra is a modular synthesizer that allows you to draw your own wave-shaping curves. It’s extremely popular because it’s intuitive, has a beginner-friendly interface, and offers abundant waveform customization options.
To create a simple oscillator in Zebra and route it through the waveshaper, draw an asymmetric wave shaping curve to introduce even harmonics, then modulate the curve’s parameters with an LFO to create a dynamic and analog-like sound.
Final Thoughts
I hope this guide helped clarify some of the confusion revolving around the so-called waveshaping tools. Manipulating audio to such an extent requires learning everything about the nature of sound and how it gets translated into digital content.
The principles of wave shaping might be hard to implement at first, but once you get a grip on them, you’ll realize this tool can greatly expand your sonic palette, and give you full control over your music production.
Have fun!