Do you have a lot of mud in your mix? Are you struggling to tame the low frequencies in your mix? You might require a trusty high pass filter. These essential mixing tools lend themselves to a wide variety of mixes, and you already have one waiting for you in your DAW!
But how does a high pass filter work? Below, we'll decode everything you need to know about using a high pass filter in your mixes and share a couple of ways that you can get started. Let's dive right into it!
What Is A High Pass Filter?
So, what is a high pass filter anyway? Essentially, a high pass filter, of HPF for short is a type of EQ filter designed to cut out extraneous low frequencies at a specific cutoff point. High pass filters are also known as low cut filters.
As you can see, the dictionary of music production made it easy on us. High pass and low cut filters cut out lower frequencies while allowing the high frequencies to come through the mix. There are different types of audio pass filters in the world of music, and you'll find these tools essentially everywhere.
HPFs can be seen on physical equipment like amplifiers, microphones, and speakers. Digital HPFs are also a staple in your DAW. You'll find them built into your eq plugin and as a part of some specialized compressors. While the high pass filters can become overused tools, if you know how to use a high pass filter properly, these handy sound shapers can certainly lead to a great mix.
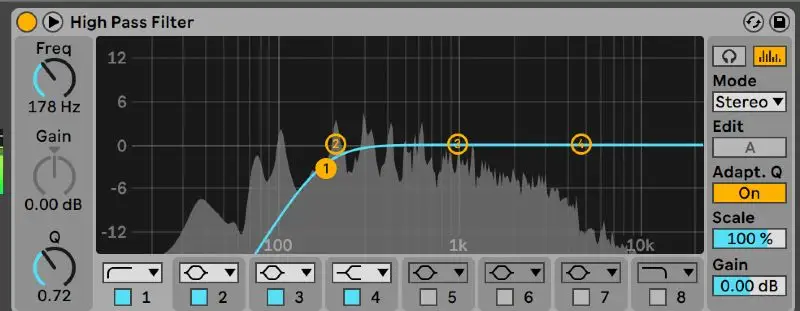
High Pass Filter EQ Vs. Low Pass Filter EQ
Generally speaking, the high pass filter and low pass filter are opposite band pass filters. The high pass filter attenuates the cutoff of unwanted low frequencies, while the low pass filter attenuates problem frequencies on the high end of the frequency spectrum. As you'll see below, the low pass filter looks like the inverse of a high pass filter or high pass eq:
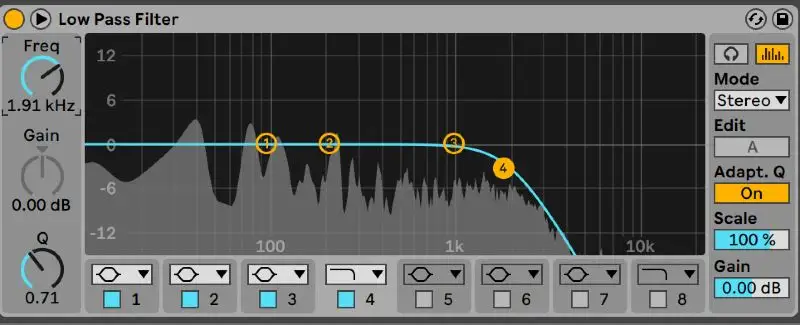
How does a high pass filter work?
A high pass filter works by creating a slope surrounding a cutoff frequency to cut out low end rumble, bring out the highs in a track, or simply create space throughout the mix. This band pass filter is designed to cut out low frequency content that is muddying up your mix . High pass filters eliminate very low frequencies making it so that noise does not pass beyond the set slope and cutoff frequencies.
Depending on your filter of choice, you can adjust the strength of this slope, the shape of your slope, and most importantly, the cutoff point at which your filter comes into play, measured in Hz.
Active Vs. Passive High Pass Filters
While there isn't necessarily a separate category for active vs. high pass filters, it's worth noting that you can use a high pass filter on a tool such as a dynamic EQ. In this way, a high pass filter could be considered "active" since it would only be coming into play when automated to do so.
A passive high pass filter, in this example, would simply adjust individual tracks to the same amount throughout a song. However, even traditional parametric eq plugins with high pass filters have properties that can be automated that you can fine-tune your listener's experience through the lens of the filters.
Analog Vs. Digital High Pass Filters
Both analog and digital high pass filters are designed to take out unwanted low frequency content in the audio signal that they're processing. That being said, it can be a little easier to program a digital high pass filter, since you may have limited bandwidth or mixing possibilities while utilizing analog equipment.
Analog equipment can have the advantage of adding a certain atmosphere of warmth that can be challenging to recreate digitally in addition to having a strong cut-off frequency for embedded high pass filters. Ultimately, both tools can be incredibly useful. You'll just need to decide which makes the most sense for your needs based on your sonic situation.
How To Use A High Pass Filter

A high pass filter, or HPF for short, isn't difficult to use but needs to be used properly so that it doesn't negatively affect the processed signal. Here is a basic guideline on how you can incorporate a high pass filter into your music properly.
1. Find your low end source and determine your goals.
To start, determine your source of low end information. Before using your high pass filter, determine your mixing goals. Are you trying to cut off all sonic information at the cutoff frequency? Or are you aiming for a more subtle sound? Take the time to think through your sonic goals for the best results.
2. Start by going too far and dial it back.
Ideally, you want to use a high pass filter as sparingly as possible since overuse can lead to a lifeless mix. Slowly adjust your low pass filter's bandwidth until you determine that the filter is too strong. Dial it back a bit from that point.
3. Check your sound in the context of the rest of the mix.
Don't forget that many filtering purposes revolve around creating space in the rest of the mix. Before committing to any specific filtering settings on your eq plugin, check to see how your altered signal sits within the rest of your session.
7 Ways To Use High Pass Filters In Mixing
When it comes to using a high pass filter, the possibilities are limitless. That being said, here are 7 key ways you can incorporate these band pass filters into your mixing technique.
- Cutting out low end rumble
- Helping other frequencies shine
- For sound automation
- Creating space for the kick drum
- Accounting for the proximity effect
- Balancing your mix
- As an easy transition during your set
1. Cutting out low end rumble
Low frequencies are notoriously challenging to tame and are easier to hear, which can lead to a lot of unnecessary frequency build-up. High pass filters can make it easy for you to cut through the noise, particularly on other instruments that don't need a lot of low information on the frequency spectrum to hold their own. For instance, you might use an HPF to cut out excess noise in the low end of a hi-hat or snare drum track to make room and clarity for parts that do need more low end information like kick drums or the bass guitar.
2. Helping other frequencies or high frequencies shine
When you cut out frequencies from one group, you help another shine or become more heard. Therefore, a high pass filter can be used as a way to promote higher frequencies in your mix. This is especially great for a vocal track where more of the high end can help create a brighter, crisper sound with more clarity.
3. For sound automation
Just like any other plugin, an HPF can be automated to create more interest throughout your mix. You can experiment with automating the cutoff frequency, bandwidth, and slope of your filter. A dynamic high pass filter can easily elevate your mix into a more dynamic, energetic one.
4. Creating space for the kick drum
There are often times when there will be a conflict between the kick drum and a bass part. So, you could use your HPF to hone in on any kick drum low frequencies that don't need to be there. Alternatively, you could automate a high pass filter or dynamic EQ to cut the bass at a certain cutoff frequency whenever the kick drum comes into play.
5. Accounting for the proximity effect
The proximity effect states that the closer a singer is to a microphone, the more low end information the recording will pick up. Therefore, you may need to use a high pass filter to accommodate for low end problem areas, especially for recording vocals . That being said, it's all very possible that you may need to revert back to the recording stage. After all, a poorly recorded main vocal track can easily break a track.
6. Balancing your mix
Creating a great mix is all about balance and choices. Therefore, it's essential to set deliberate cutoff frequency points that speak to the needs of your instruments in context with each other. It may make sense to approach each section of your mix by frequency range. For instance, you may approach the instruments in low, mid, and high frequency groups each in separate sections.
From there, you can determine the cutoff frequency needed for each instrument within these groups to help the most important track
7. As an easy transition during your set
Band pass filters and shelving filters alike can both make amazing, simple yet sufficient transitions in DJ sets or mixtapes. Don't forget to experiment with attenuating these filters in context from one song to another. You can also automate your low cut filter to an analog mixing knob for some extra playing power.

Other Uses Of High Pass Filters In Music
Essentially, the sky is the limit with high pass filters throughout the recording, mixing , and mastering process! That being said, use these tools carefully as they can be one of the most overused tools in music. Don't cut out audio signals' low end energy if you don't need to.
One example of other ways to use HPFs in your music is to place these band pass filters on reverb or delay tracks. This is because it's often better to use these reflection plugins on high end frequency ranges than lower ones. It's also a good idea to think of using a high pass filter in the context of your full effect chain.
For example, using a particular compressor may cause unwanted build up on your instruments. You may have to compensate in your mix by adding a high pass filter after the processed signal in your mix chain.
High Pass Filter FAQs
Are you still struggling to understand the magic of high pass filters? Here are some commonly asked questions and answers to expand your understanding.
What is a high pass filter used for?
A high pass filter or low cut filter is used to cut out or lower the impact of lower frequencies. Low end frequencies can be notorious for producing mud if not processed properly. High pass filters help tame this region without overly processing a sound.
Where do I put a high pass filter?
You should use a high pass filter wherever you notice too many low end frequencies. You can use a high pass filter on just about any instrument as long as your crossover point isn’t so strong that it takes away the life of a sound.
Should I use high pass filter for vocals?
It’s very common to use a high pass filter on vocals since they can carry a lot of unnecessary low end information. That being said, you need to be careful while using a high pass filter on vocals since you can easily go too far and take the energy out of your audio.
How does a high pass filter work on an amplifier?
High pass filters built into playback devices and amplifiers work in the same way they would in your DAW . They aim to cut out extraneous low-end frequencies in between preamp and amplifier creating a cleaner sound or different styles of the same signal.
Do high pass filters have bandwidth?
Yes! Any filter type has a bandwidth that can be adjusted based on the needs of the particular sound. The smaller the bandwidth of a high pass filter, the more low end frequencies you’re cutting out. Greater bandwidth allows for more frequencies to pass through.
Is a high pass filter the same as a crossover?
A crossover filter can be used to isolate a speaker’s signal to different frequency ranges. A high pass filter is typically used in a more electronic setting, focusing entirely on cutting out the low end range of an audio signal.
What is the difference between high pass and low pass filters?
The difference between high and low pass filters is based on what they intend to cut out in terms of frequencies. Low pass filters are used to cut out extraneous higher frequencies. High pass filters are designed to cut out extra low end frequencies.
How do you use high pass filter on vocals?
You have to be particularly careful while using a high pass filter on vocals. It’s all too easy to cut out too much low end, leaving your audio signal without any energy or emotion. Pull back the bandwidth on your high pass filter slowly on vocals until you reach the point where it’s gone too far and dial it back.
What is the impedance of a high pass filter?
Impedance will vary greatly depending on your specific audio equipment, regardless of whether they utilize a high pass filter. Typically, audio devices with higher input impedances can be driven by a low amount of power making them more desired in live settings.
What does a high pass crossover do?
Just like a high pass filter, a high pass crossover aims to cut out unwanted low end frequencies. Typically, a high pass crossover allows frequencies in the 5kHz-20kHz range while omitting all other parts of the signal. This helps keep the playback output as clean as possible.
As you can see, there are plenty of ways to use the versatile high pass filter in your mix and music production workflow. Hopefully, this HPF guide makes it easier for you to incorporate this powerful tool into your sessions. Happy mixing!